Atom with a charge crossword – Delve into the intriguing world of atoms with a charge! This crossword puzzle unravels the mysteries of charged atoms, their types, causes, consequences, and practical applications. Embark on a captivating journey to unravel the secrets of matter and its interactions.
Atoms, the fundamental building blocks of our universe, possess a fascinating ability to acquire an electrical charge. Discover the mechanisms behind this phenomenon and explore the diverse types of charged atoms, each with unique characteristics and properties.
Definition of Atom with a Charge
An atom with a charge, also known as an ion, is an atom that has lost or gained electrons, resulting in a net electrical charge.
When an atom loses electrons, it becomes positively charged and is called a cation. Conversely, when an atom gains electrons, it becomes negatively charged and is called an anion.
Examples of Atoms with a Charge
Examples of cations include:
- Sodium ion (Na+)
- Potassium ion (K+)
- Calcium ion (Ca2+)
- Magnesium ion (Mg2+)
Examples of anions include:
- Chloride ion (Cl-)
- Fluoride ion (F-)
- Bromide ion (Br-)
- Iodide ion (I-)
Types of Atoms with a Charge
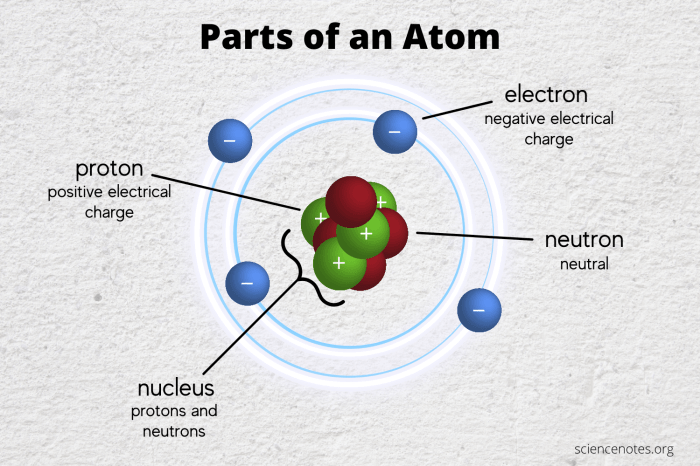
Atoms with a charge, also known as ions, are classified into two main types: cations and anions.
Cations
Cations are atoms that have lost one or more electrons, resulting in a positive charge. They are formed when an atom loses electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Anions
Anions are atoms that have gained one or more electrons, resulting in a negative charge. They are formed when an atom gains electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Causes of Atoms Acquiring a Charge
Atoms can acquire a charge through various processes. One common cause is the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions. When an atom gains or loses electrons, its overall charge becomes unbalanced, creating an ion with a net positive or negative charge.
Electron Transfer
Electron transfer can occur through several mechanisms:
- Chemical Reactions:In chemical reactions, atoms can exchange electrons to form stable compounds. For example, when sodium (Na) reacts with chlorine (Cl), Na transfers an electron to Cl, forming Na+ and Cl- ions.
- Electrochemical Processes:Electrolysis and electrochemical cells involve the transfer of electrons between electrodes and ions in solution. During electrolysis, an electric current drives the movement of electrons, causing atoms to gain or lose electrons.
- Triboelectric Charging:When two materials are rubbed together, electrons can be transferred from one material to the other. This process is commonly observed in everyday phenomena such as static electricity.
Consequences of Atoms Having a Charge
Atoms with a charge, known as ions, exhibit unique chemical and physical properties that significantly impact their behavior and interactions. The presence of a charge alters the way they react with other atoms and molecules, influencing their chemical bonding, solubility, and other characteristics.
Chemical Properties
Charged atoms have altered chemical reactivity due to their electrostatic attraction or repulsion. Positively charged ions (cations) are attracted to negatively charged ions (anions), forming ionic bonds. This attraction drives the formation of ionic compounds, such as sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium iodide (KI).
Conversely, ions with the same charge repel each other, affecting the solubility and stability of compounds.
Physical Properties
The charge of an atom also affects its physical properties. Charged atoms experience electrostatic forces that influence their movement and interactions. For example, ions in solution can move freely under the influence of an electric field, a phenomenon known as electrolysis.
Searching for the solution to an “atom with a charge” crossword clue? Take a break and immerse yourself in the poignant world of night calls by lisa fugard . When you return, you’ll find the answer effortlessly, as the play’s exploration of human connection and isolation will sharpen your mind and provide fresh perspectives.
Additionally, charged atoms can exhibit magnetic properties, as seen in ferromagnetic materials like iron, where the alignment of charged atoms creates a magnetic field.
Interactions with Other Atoms and Molecules, Atom with a charge crossword
Charged atoms interact with other atoms and molecules through electrostatic forces. These interactions can range from weak van der Waals forces to strong ionic bonds. The charge of an atom determines the strength and nature of these interactions, affecting the formation of chemical bonds, the solubility of compounds, and the behavior of molecules in solution.
Applications of Atoms with a Charge
Atoms with a charge, also known as ions, have a wide range of practical applications in various fields, including medicine, technology, and manufacturing.
Their unique properties, such as their ability to conduct electricity and interact with magnetic fields, make them essential components in many modern technologies.
Medical Applications
- Radiation Therapy:Charged atoms, such as protons and carbon ions, are used in radiation therapy to target and destroy cancerous cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
- Medical Imaging:Ions are also used in medical imaging techniques like X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures.
- Drug Delivery:Charged atoms can be used to deliver drugs directly to specific cells or tissues, improving drug efficacy and reducing side effects.
Technological Applications
- Batteries:Ions are essential components in batteries, where they facilitate the flow of electrons between electrodes, generating electricity.
- Fuel Cells:Fuel cells utilize charged atoms to produce electricity through electrochemical reactions, offering a clean and efficient alternative energy source.
- Plasma Displays:Plasma displays rely on charged atoms to create images by exciting gas molecules, resulting in the emission of light.
Manufacturing Applications
- Ion Implantation:Charged atoms are implanted into materials to modify their electrical and optical properties, enhancing their performance in electronic devices.
- Electroplating:Charged atoms are used in electroplating processes to deposit metal coatings on various surfaces, improving their durability and conductivity.
- Ion Etching:Charged atoms can be used to etch materials with high precision, creating intricate patterns and structures in semiconductor fabrication.
Answers to Common Questions: Atom With A Charge Crossword
What is an atom with a charge?
An atom with a charge, also known as an ion, is an atom that has lost or gained electrons, resulting in an imbalance between its positive and negative charges.
What causes an atom to acquire a charge?
Atoms can acquire a charge through various processes, such as electron transfer, friction, or chemical reactions.
What are the consequences of an atom having a charge?
Charged atoms exhibit unique chemical and physical properties, affecting their reactivity, bonding behavior, and interactions with other atoms and molecules.