Osmosis and diffusion test questions – Embark on an in-depth exploration of osmosis and diffusion with our comprehensive test questions. This guide delves into the intricacies of these fundamental processes, providing a thorough assessment of your understanding.
From the mechanisms of osmosis and diffusion to their real-world applications, this resource equips you with the knowledge and skills to excel in your studies and beyond.
Osmosis
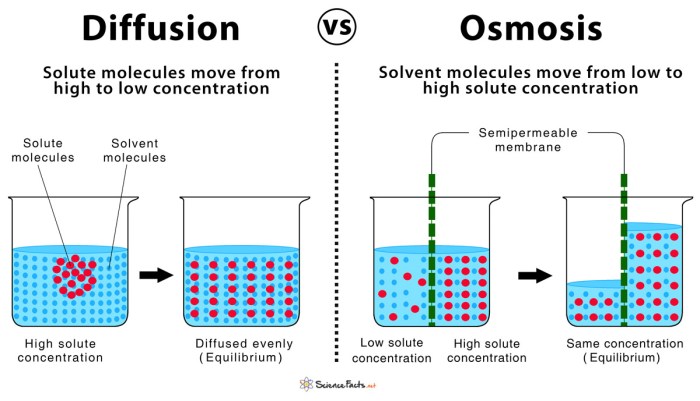
Osmosis is a passive transport process in which water molecules move across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. The semipermeable membrane allows water molecules to pass through, but it prevents the passage of other substances, such as ions and molecules.
Factors Affecting Osmosis
The rate of osmosis is affected by several factors, including:
- Concentration Gradient:The greater the concentration gradient of water molecules across the membrane, the faster the rate of osmosis.
- Temperature:The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of osmosis.
- Surface Area of the Membrane:The larger the surface area of the membrane, the faster the rate of osmosis.
- Thickness of the Membrane:The thicker the membrane, the slower the rate of osmosis.
Examples of Osmosis
Osmosis plays an important role in many biological processes, including:
- Water absorption by plants:Plants absorb water from the soil through their roots by osmosis.
- Regulation of cell volume:Cells use osmosis to regulate their volume by controlling the flow of water across their cell membranes.
- Exchange of nutrients and waste products:Osmosis allows nutrients to enter cells and waste products to leave cells.
Diffusion
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. It is a passive process, meaning that it does not require energy. Diffusion is driven by the random motion of molecules and the tendency for molecules to move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated.
Factors that Affect Diffusion
- Concentration gradient:The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion.
- Temperature:The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of diffusion.
- Surface area:The greater the surface area, the faster the rate of diffusion.
- Distance:The greater the distance, the slower the rate of diffusion.
Examples of Diffusion in Real-Life Situations
- The spreading of a perfume in a room
- The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs
- The movement of nutrients from the soil into plant roots
- The movement of water from a high-pressure area to a low-pressure area
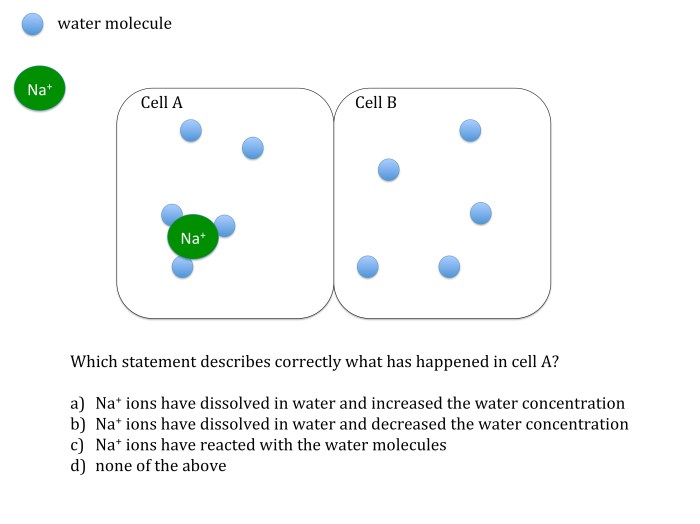
Osmosis and Diffusion Test Questions
Test questions are essential for evaluating students’ understanding of osmosis and diffusion. These questions should assess students’ knowledge of the key concepts, principles, and applications of these processes.
Test Questions, Osmosis and diffusion test questions
- Define osmosis and explain the factors that affect its rate.
- Describe the process of diffusion and explain how it differs from osmosis.
- Explain the role of semipermeable membranes in osmosis and diffusion.
- Predict the direction of water movement across a semipermeable membrane in different solutions.
- Design an experiment to demonstrate the principles of osmosis or diffusion.
- Explain the applications of osmosis and diffusion in biological systems and everyday life.
Answer Key
- Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. The rate of osmosis is affected by the concentration gradient, the surface area of the membrane, and the temperature.
- Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. It differs from osmosis in that it involves the movement of particles other than water.
- Semipermeable membranes allow water molecules to pass through but block the passage of larger molecules. They play a crucial role in osmosis and diffusion by controlling the movement of water and other substances across the membrane.
- The direction of water movement across a semipermeable membrane is determined by the concentration gradient. Water moves from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration.
- An experiment to demonstrate the principles of osmosis can be designed using a U-tube filled with water and a semipermeable membrane separating the two arms. A solution of different concentrations is added to one arm, and the movement of water across the membrane is observed.
- Osmosis and diffusion have numerous applications in biological systems and everyday life. For example, osmosis is involved in the absorption of water by plants and the movement of nutrients into and out of cells. Diffusion is involved in the exchange of gases in the lungs and the absorption of nutrients in the digestive system.
Osmosis and Diffusion in the Classroom
Teaching osmosis and diffusion in the classroom can be made engaging and interactive through various demonstrations and hands-on activities. These activities allow students to visualize and understand the concepts in a practical way.
One effective way to demonstrate osmosis is through the “raisin rehydration” experiment. Students soak raisins in water and observe how they swell and become plump. This illustrates the movement of water molecules from a region of high concentration (water) to a region of low concentration (inside the raisin).
Diffusion Demonstrations
- Diffusion in Liquids:Students place a drop of food coloring in a beaker of water and observe how the color spreads throughout the liquid over time. This demonstrates the movement of solute particles from an area of high concentration (the drop) to an area of low concentration (the water).
- Diffusion in Gases:Students use perfume or scented oil to demonstrate diffusion in gases. When a small amount of perfume is released in a room, the scent gradually spreads throughout the space, illustrating the movement of gas particles from an area of high concentration (near the source) to an area of low concentration (away from the source).
Lesson Plans and Activities
- Osmosis Simulation:Students create a model of a cell membrane using a semipermeable bag (e.g., a dialysis bag) and fill it with a sugar solution. They then place the bag in a beaker of water and observe the changes in the bag’s size and the movement of water molecules.
- Diffusion Lab:Students investigate the factors that affect the rate of diffusion by varying the temperature, concentration gradient, and surface area of the diffusion medium. They measure the rate of diffusion using techniques such as spectrophotometry or chromatography.
Osmosis and Diffusion in the Real World
Osmosis and diffusion are fundamental processes that occur in various aspects of everyday life and play crucial roles in biological systems.
One prominent example of osmosis in the real world is the preservation of food through pickling. In this process, vegetables are submerged in a concentrated salt solution, which creates a hypertonic environment. This causes water to move out of the vegetables by osmosis, resulting in the withdrawal of water from the plant cells and the prevention of bacterial growth.
Diffusion in Everyday Life
Diffusion is another significant process with numerous real-world applications. One example is the spreading of scents. When a perfume is sprayed into the air, the fragrance molecules diffuse throughout the room, allowing us to perceive the scent.
Importance in Biological Systems
In biological systems, osmosis and diffusion are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and proper functioning. Osmosis regulates the movement of water across cell membranes, ensuring that cells maintain their optimal hydration levels. Diffusion facilitates the exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste products between cells and their surroundings, supporting metabolic processes and waste removal.
Key Questions Answered: Osmosis And Diffusion Test Questions
What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration, while diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
What factors affect the rate of osmosis?
The rate of osmosis is affected by the concentration gradient, temperature, surface area of the membrane, and the permeability of the membrane.
What are some examples of osmosis in real life?
Examples of osmosis in real life include the absorption of water by plants, the movement of water across cell membranes, and the desalination of seawater.