Pleural fluid mesothelial cells vs macrophage – Pleural fluid mesothelial cells and macrophages are critical players in the pleural space, exhibiting distinct characteristics and roles in pleural effusions. Understanding their interplay is essential for accurate diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic management of pleural diseases.
These cells contribute to the formation, resolution, and inflammatory response of pleural effusions. Their presence or absence aids in differentiating between different types of pleural effusions, providing insights into the underlying disease process and guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Characteristics of Pleural Fluid Mesothelial Cells vs Macrophages
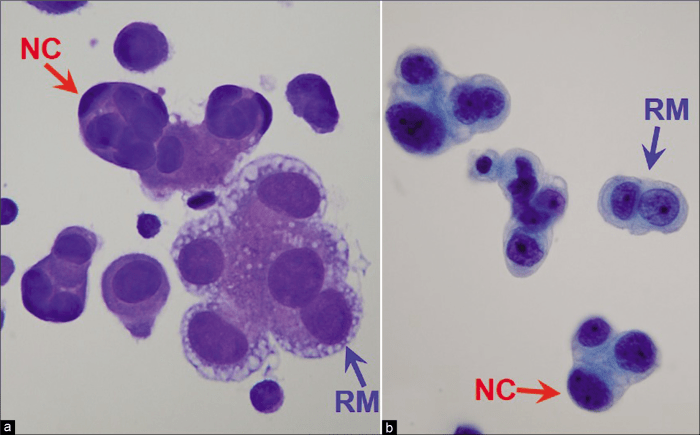
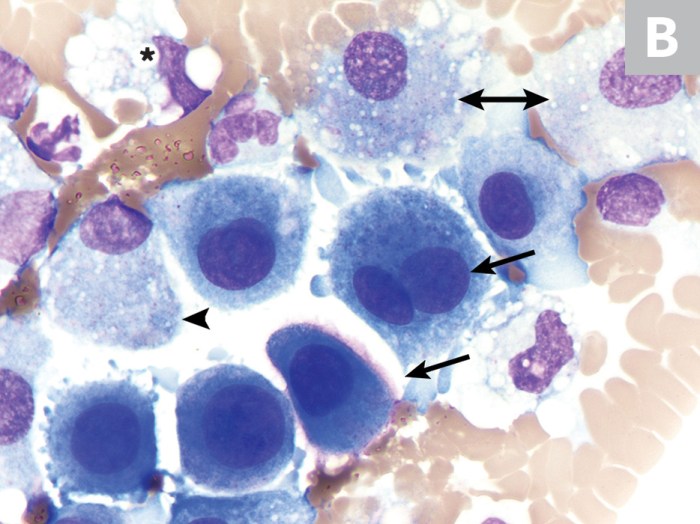
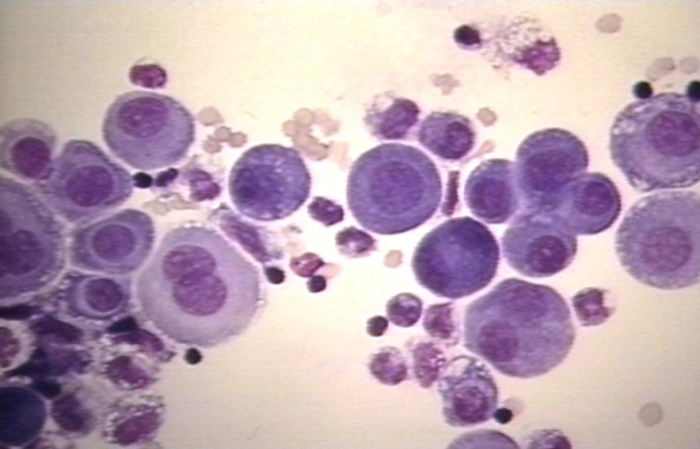
Pleural fluid mesothelial cells and macrophages are two distinct cell types that reside in the pleural space. They exhibit unique morphological and functional characteristics that contribute to their respective roles in pleural physiology and disease.
Morphological Differences:
- Mesothelial cells:Flattened, polygonal cells with a central nucleus and abundant cytoplasm. They line the pleural surfaces and secrete hyaluronic acid to maintain pleural lubrication.
- Macrophages:Round or irregular cells with a large, indented nucleus and abundant cytoplasm. They are highly phagocytic and play a crucial role in the immune response within the pleural space.
Table: Key Characteristics of Pleural Fluid Mesothelial Cells vs Macrophages
| Characteristic | Mesothelial Cells | Macrophages |
|---|---|---|
| Morphology | Flattened, polygonal | Round or irregular |
| Nucleus | Central, round | Large, indented |
| Cytoplasm | Abundant | Abundant |
| Function | Secrete hyaluronic acid, maintain pleural lubrication | Phagocytic, immune response |
Frequently Asked Questions: Pleural Fluid Mesothelial Cells Vs Macrophage
What are the key morphological differences between pleural fluid mesothelial cells and macrophages?
Mesothelial cells are larger and polygonal, with prominent nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm. Macrophages are smaller and round, with a more condensed nucleus and less cytoplasm.
How do pleural fluid mesothelial cells contribute to the formation and resolution of pleural effusions?
Mesothelial cells secrete pro-inflammatory mediators that promote fluid accumulation, while also producing anti-inflammatory factors that aid in effusion resolution.
What is the diagnostic significance of pleural fluid mesothelial cells and macrophages in differentiating between different types of pleural effusions?
The presence of mesothelial cells suggests a reactive effusion, while their absence may indicate a neoplastic or inflammatory process. Macrophages are typically present in inflammatory effusions, and their number can indicate the severity of inflammation.