Imagine you have some workers and some handheld computers. What could you achieve if you could seamlessly integrate these two elements to enhance productivity and efficiency? This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of handheld computers in the workplace, exploring their benefits, challenges, and best practices for implementation.
From workforce analysis and device selection to software integration and performance monitoring, we will cover every aspect of leveraging handheld computers to empower your workforce and drive business success.
Workforce Analysis
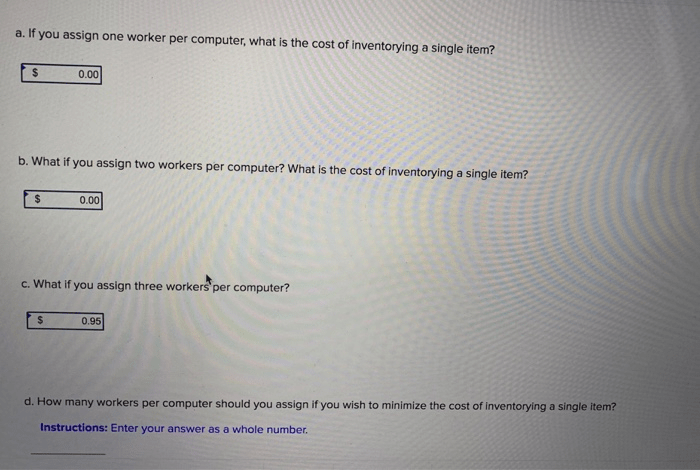
Equipping workers with handheld computers offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance productivity and efficiency in the workplace.
Firstly, handheld computers provide workers with real-time access to critical information, such as product specifications, inventory levels, and customer data. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces errors, leading to improved accuracy and time savings.
Secondly, handheld computers facilitate communication and collaboration among workers. They can be used to send messages, share files, and schedule appointments, enabling seamless coordination and teamwork.
However, it is important to acknowledge potential challenges associated with implementing handheld computers in the workplace. These include the cost of devices, the need for training, and the potential for security risks.
Device Selection
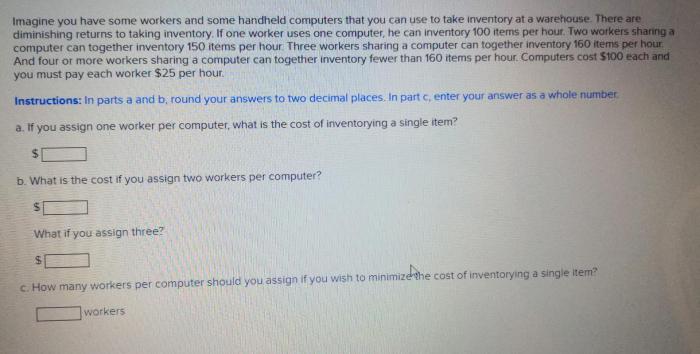
When selecting handheld computers for workers, several key features should be considered:
- Operating System:The operating system determines the functionality and compatibility of the device with various software applications.
- Screen Size and Resolution:The screen size and resolution impact the visibility and readability of information displayed on the device.
- Battery Life:The battery life should be sufficient to support extended usage throughout the workday.
- Durability:The device should be rugged and durable enough to withstand the rigors of the workplace environment.
- Size and Weight:The size and weight of the device should be comfortable for workers to carry and use for extended periods.
There are various types of handheld computers available in the market, including smartphones, tablets, and dedicated rugged devices. Smartphones offer a balance of functionality and affordability, while tablets provide larger screens for improved visibility. Rugged devices are specifically designed for harsh environments and offer enhanced durability.
The most suitable handheld computer for a specific work requirement depends on factors such as the industry, job function, and the specific tasks that need to be performed.
Software Integration
Integrating handheld computers with existing software systems is crucial for maximizing their value and ensuring seamless data flow within the organization.
When selecting software for handheld computers, compatibility with the device’s operating system is essential. Additionally, the software should provide the necessary functionality to support the specific tasks performed by the workers.
Integrating handheld computers with other systems can present challenges, such as data security and synchronization issues. To address these challenges, it is important to implement robust security measures and establish clear protocols for data transfer.
Training and Implementation
A comprehensive training program is essential to ensure that workers are proficient in using handheld computers and can maximize their benefits.
The training program should cover the following aspects:
- Device Familiarization:Training workers on the basic functions and features of the handheld computers.
- Software Functionality:Instructing workers on how to use the specific software applications installed on the devices.
- Workflow Integration:Demonstrating how to incorporate handheld computers into existing workflows and processes.
In addition to training, a detailed implementation plan should be developed to ensure a smooth rollout of handheld computers in the workplace. This plan should include steps for device deployment, software installation, and user support.
A communication strategy should also be created to inform workers about the benefits and usage of handheld computers. This strategy can include presentations, newsletters, and training materials.
Performance Monitoring and Evaluation
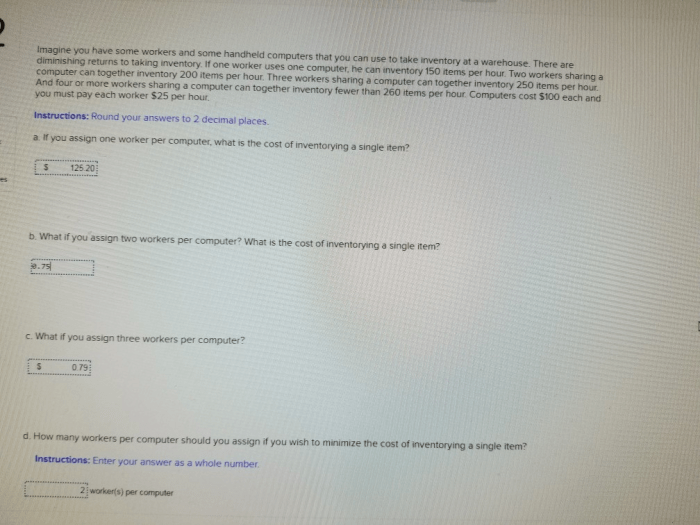
Measuring the impact of handheld computers on worker productivity is essential to justify the investment and identify areas for improvement.
Metrics for measuring productivity can include:
- Task Completion Time:The time it takes workers to complete specific tasks using handheld computers compared to traditional methods.
- Error Rate:The number of errors made by workers using handheld computers compared to traditional methods.
- Customer Satisfaction:Feedback from customers regarding the efficiency and responsiveness of workers using handheld computers.
Regular tracking and evaluation of handheld computer usage can provide valuable insights into their effectiveness and identify areas where further training or support is needed.
Questions Often Asked: Imagine You Have Some Workers And Some Handheld Computers
What are the key benefits of equipping workers with handheld computers?
Handheld computers offer numerous benefits, including improved data accuracy, real-time communication, increased efficiency, enhanced collaboration, and optimized decision-making.
How do I choose the right handheld computers for my workers?
Consider factors such as operating system, screen size, battery life, ruggedness, and compatibility with existing software systems when selecting handheld computers.
What are the challenges of implementing handheld computers in the workplace?
Potential challenges include user adoption, training requirements, data security concerns, and the need for ongoing support and maintenance.